- Organizations can
undertake high-profile strategic initiatives including
- Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Supply Chain Management - involves the management of information flows
between and among stages in a supply chain to maximize total supply chain
effectiveness and profitability
Four basic components of supply chain
management include :
- Supply chain strategy - strategy for managing all the resources required to meet customer demand for all products and services
- Supply chain partners - the partners chosen to deliver finished products, raw materials, and services including pricing, delivery, and payment processes along with partner relationship monitoring metrics
- Supply chain operation - the schedule for production activities including testing, packaging, and preparation for delivery. Measurements for this component include productivity and quality
- Supply chain logistics - the product delivery processes and elements including orders, warehouses, carriers, defective product returns, and invoicing
- Effective and efficient supply chain management systems can enable the organization to :
- Decrease the buyer power
- Increase supplier power
- Increase switching costs
- Create entry barriers
- Increase efficiencies while seeking a competitive advantage through cost leadership
 |
| Effective and efficient supply chain managements effect on Porter's Five Forces |
2. Customer Relationship Management - involves managing all aspects of a customer's relationship with an organization to increase customer loyalty and retention and an organization's profitability
- CRM is not just
technology, but a strategy, process, and business goal that an organization
must embrace on an enterprisewide level
- CRM can enable the organization to
- identify types of customers
- design individual customer marketing campaigns
- treat each customer as an individual
- understand customer buying behaviours
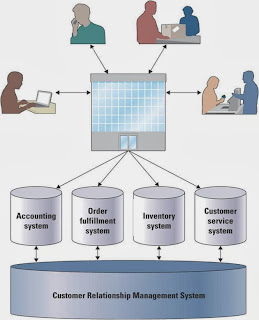 |
| CRM overviews |
3. Business Process Reenginering - analysis and redesign of workflow within and between the enterprise
- The purpose of BPR is to make all business processes best-in-class
- Finding opportunity using BPR
- Types of change an
organization can achieve, along with the magnitudes of change and the potential
business benefit
4. Enterprise Resource Planning - integrates all departments
and functions throughout an organization into a single IT system so that
employees can make decisions by viewing enterprisewide information on all business operations
- ERP systems collect data from across an
organization and correlates the data generating an enterprisewide
view





