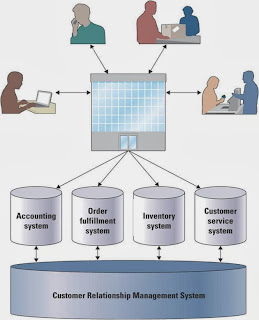
Information technology's impact on business operation
- Information Technology (IT) - a field concerned with the use of technology in managing and processing information
- important enabler of business success and innovation
- Management Information Systems (MIS) - a general name for the business function and academic discipline covering the application of people, technologies, and procedures to solve business problems
- business function, similar to accounting, finance, operations and human resources
- When beginning to learn about information technology it is important to understand
- data, information, and business intelligence IT resources
- IT cultures
- Data - raw facts that describe the characteristics of an event
- Information - data converted into a meaningful and useful context
- Business intelligence - applications and technologies that are used to support decision making efforts
 |
| People use information technology to work with information |
- Organizational information cultures :
- Information-Functional Culture - employees use information as a means of exercising influence or power over others
- Information-Sharing Culture - employees across departments trust each other to use information to improve performance
- Information-Inquiring Culture - employees across departments search for information to better understand the future and align themselves with current trends and new directions
- Information-Discovery Culture - employees across departments are open to new insights about crisis and radical changes and seek ways to create competitive advantages